Hip Impingement (Femoroacetabular Impingement Or FAI)
Overview
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), also called hip impingement, occurs when abnormal contact between the femoral head (ball) and acetabulum (socket) causes friction in the hip joint. This friction can damage the articular cartilage (the smooth surface of the ball and socket) or the labral tissue (the cartilage lining the rim of the socket).
Over time, repeated friction can lead to:
- Labral tears
- Cartilage fraying
- Progressive joint damage
If left untreated, this can eventually lead to bone-on-bone contact, a hallmark of hip osteoarthritis.
Abnormal Hip Bone Prominences
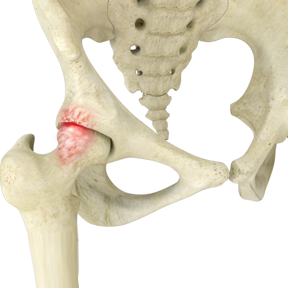
FAI typically occurs in two forms:
CAM Impingement
- The femoral head and neck are not perfectly round, usually due to excess bone formation.
- This irregularity causes abnormal contact between the femoral head and acetabulum.
PINCER Impingement
- The acetabulum (hip socket) rim overgrows, covering too much of the femoral head.
- This pinches the labral cartilage and may also occur if the hip socket is abnormally angled.
Mixed FAI
- Most patients have a combination of CAM and PINCER morphology.
Symptoms of FAI
Common symptoms include:
- Groin pain during hip activity
- Pain in the front, side, or back of the hip
- Dull ache or sharp pain
- Locking, clicking, or catching in the hip
- Pain after prolonged sitting or walking
- Difficulty walking uphill
- Restricted hip motion
- Low back pain
- Pain in the buttocks or outer thigh
Risk Factors for Developing FAI
Factors that increase the likelihood of FAI include:
- High-impact athletes (football, hockey, weightlifting)
- Jobs requiring repetitive hip flexion or heavy labor
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Anatomical abnormalities of the femoral head or hip angle
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease in childhood
- Hip trauma
- Inflammatory arthritis
How FAI is Diagnosed
Evaluation by an orthopedic hip specialist is critical. Diagnostic methods include:
- Detailed medical history
- Physical examination
- Imaging studies: X-rays, MRI, CT scan, and ultrasound
Treatment Options
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Management
Non-surgical options may relieve symptoms but do not correct the underlying bony abnormalities. They include:
- Activity modification and rest
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Corticosteroid or anesthetic injections into the hip
Surgical Treatment
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure to:
- Repair or debride labral tears
- Resection bony prominences causing impingement
- Release and reattach the labrum if necessary
- Repair subtle hip instability by capsular plication
What Is done in hip arthroscopy? The procedure is performed to address the impingement bony prominences and to repair or reconstruct the labrum tear in the hip joint when conservative treatment measured fail to provide relief to the patient. The tear can be repaired or debrided using this minimally invasive approach. If the labrum can be repaired, sutures are placed to re-appose the labrum to the acetabulum to allow healing to the bone. The labrum may need to be temporarily released from the acetabulum in some cases to allow for complete impingement resection. The bony prominences causing the impingement of the femoral neck and acetabulum can be resected. This can improve the hip pain and restore the hip range of motion. The most common location of these prominences makes them accessible with standard hip arthroscopic techniques. In certain conditions, a formal open approach must be performed. At the conclusion of the case, the hip capsule tissues may be sutured closed. In patient with subtle instability, the capsule may be plicated to reduce the volume of the hip joint
Open surgery may be required for extensive deformities or complex cases.
Indications for hip arthroscopy include:
- Symptomatic FAI (pain with hip flexion/internal rotation)
- Positive impingement test
- Imaging confirming cam/pincer morphology
- Labral tear on MRI
- Minimal or no osteoarthritis
- Failed conservative treatment for ≥3 months
Effectiveness of Hip Arthroscopy
- Short-term outcomes (2–5 years): 68–96% of patients report good-to-excellent results
- Long-term outcomes (10 years): ~90% patient satisfaction and 91.6% survivorship
- Pain and function scores improve by 20–35 points (HOS, iHOT-33, mHHS)
- Athletes: 75–90% return to sport, ~70% return to pre-injury level
- Labral repair consistently shows superior outcomes compared to labral debridement
Patient Selection is Key:
Best results are seen in patients who are:
- Younger (<40 years old)
- Highly active
- Minimal cartilage damage (Outerbridge grade 0–2)
- Symptom duration <2 years
- No osteoarthritis (Tonnis grade 0–1)
- CAM lesion present (better outcomes than isolated pincer lesion)
Why Choose an OrthoMiami Physician for Your FAI Surgery
OrthoMiami physicians are fellowship-trained in hip preservation with extensive experience in treating FAI. Our team emphasizes:
- Evidence-based, individualized treatment planning
- Advanced 3-D imaging to map bony morphology and labral tears
- Precision correction of cam and pincer lesions
- Minimally invasive arthroscopic or open techniques tailored to your anatomy
- Commitment to restoring hip function and delaying or preventing arthritis
Why Choose Dr. J. Pieter Hommen to Treat Your Hip Impingement
A Thoughtful, Joint-Preserving Approach
Dr. Hommen brings over 20 years of hip arthroscopy experience and serves as a leader in hip preservation. His philosophy on the treatment of hip impingement is rooted in precision, restraint, and long-term thinking. He views hip arthroscopy not as a one-size-fits-all solution, but as a powerful tool when applied thoughtfully and supported by high-quality evidence. By combining meticulous patient selection, modern arthroscopic techniques, and an unwavering commitment to evidence-based medicine, Dr. Hommen strives to deliver outcomes that relieve pain, restore performance, and protect the hip joint for years to come.
Dr. J. Pieter Hommen’s Philosophy on Treating FAI
Dr. J. Pieter Hommen approaches the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) with a clear, evidence-based philosophy: the right procedure, for the right patient, at the right time. His goal is not simply to address pain, but to restore durable hip function, preserve the native joint, and allow patients—especially active individuals and athletes—to safely return to the activities that matter most to them.
Evidence-Based Use of Hip Arthroscopy
The medical literature strongly supports hip arthroscopy as an effective treatment for appropriately selected patients with FAI. Dr. Hommen also emphasizes modern hip preservation principles supported by the literature, including the clear superiority of labral repair over labral debridement, which has been shown to result in better pain relief, improved function, and enhanced long-term joint preservation.
Meticulous Patient Selection as the Cornerstone of Success
Central to Dr. Hommen’s philosophy is the understanding that patient selection is the single most important predictor of successful outcomes in hip arthroscopy. Evidence consistently demonstrates improved results in patients with favorable clinical and structural characteristics. Dr. Hommen carefully evaluates each patient using advanced imaging, detailed physical examination, and a thorough review of clinical history to ensure that surgery is offered only when the probability of a meaningful, durable benefit is high.
Precision Through Advanced Imaging and Intraoperative Guidance
An essential part of Dr. Hommen’s philosophy is precision correction of the underlying bony impingement, guided by advanced technology. He routinely utilizes preoperative three-dimensional imaging to comprehensively map each patient’s unique femoroacetabular anatomy and accurately define the location, extent, and morphology of cam and pincer lesions. This allows for individualized surgical planning rather than a generalized or "one-size-fits-all" approach.
During surgery, Dr. Hommen incorporates intraoperative computer-guided and imaging-assisted techniques to confirm accurate resection and contouring of the femoral head-neck junction and acetabular rim in real time. This approach is supported by the literature, which demonstrates that adequate—but not excessive—resection is critical to optimizing outcomes, reducing residual impingement, and minimizing the risk of revision surgery. By combining 3D preoperative planning with intraoperative guidance, Dr. Hommen aims to restore normal hip mechanics with the highest level of accuracy while preserving healthy bone and cartilage.
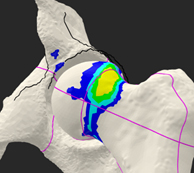
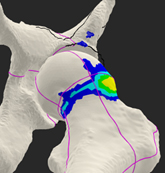
Case Example
Patient: 22-year-old soccer player with progressive hip pain
- History: Hip injury from a free kick, unsuccessful conservative management
- Findings: Cam lesion, anterior inferior iliac spine avulsion fracture, and labral tear
- Procedure: Arthroscopic resection of bony fragment, cam resection, labral repair
- Outcome: Pain-free with restored hip motion and no residual symptoms and is playing soccer pain-free.
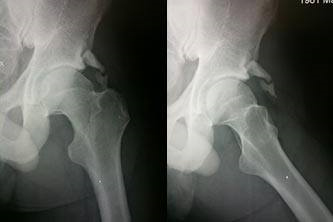 Prior to Resection of the Impingement Lesion
Prior to Resection of the Impingement Lesion
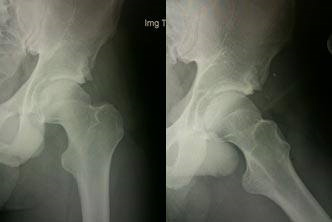 After Arthroscopic Impingement Resection
After Arthroscopic Impingement Resection













